FROM OUR BLOG
FROM OUR BLOG
FROM OUR BLOG
From Data to Digital Sound: The Evolution of AI-Powered Music Creation and Its Impact on the Industry
Dec 15, 2025


The Rise of Data-Driven Music Creation
In the past decade, music production started a transformation. Traditional methods relied on human composers, musicians, and physical instruments. Now, data-driven tools and artificial intelligence (AI) are reshaping the process. AI music creators are growing more powerful and accessible. These systems rely heavily on large datasets and smart algorithms. The result: anyone can generate music with a few clicks. This trend is changing how music is made, distributed, and consumed.
The Challenge in Conventional Music Production
Producing professional music is costly and slow. It needs skilled musicians, studios, equipment, and time. Independent artists or small teams often lack these resources. Also, coordinating multiple tracks, mixing, mastering, and licensing makes things complex. For many creators, producing original music remains out of reach. This limits diversity, slows release frequency, and raises entry barriers.
Moreover, as streaming platforms and social media drive demand for new songs constantly, traditional workflows struggle to keep up. Artists may feel pressured to churn out content quickly. In such a fast-paced context, old methods are inefficient. There is a clear need for tools that can speed up music creation, reduce cost, and simplify licensing.
How Smart Data Powers AI Music Tools
At the core of modern AI music generators lies data — lots of it. High-fidelity music recordings, MIDI data, metadata, genre tags, and structural annotations feed machine-learning models. Models learn patterns: chord progressions, rhythms, instrumentation, genre characteristics. With enough training data, AI can generalize: it can create original compositions that follow genre conventions. This helps the AI produce music that feels coherent and professional.
For example, open-source research frameworks like Music Representing Corpus Virtual (MRCV) enable experiments in generative music, sound design, and virtual instrument creation. They show how leveraging curated datasets helps generate diverse music and sound assets.
Similarly, advanced models such as those behind OpenMusic AI use diffusion-based or deep learning approaches, trained on large, high-quality audio datasets. These systems can handle multi-track harmony, realistic instrumentation, and varied genres — not just simple looped beats. This data grounding allows AI to “understand” the building blocks of music before recombining them creatively.
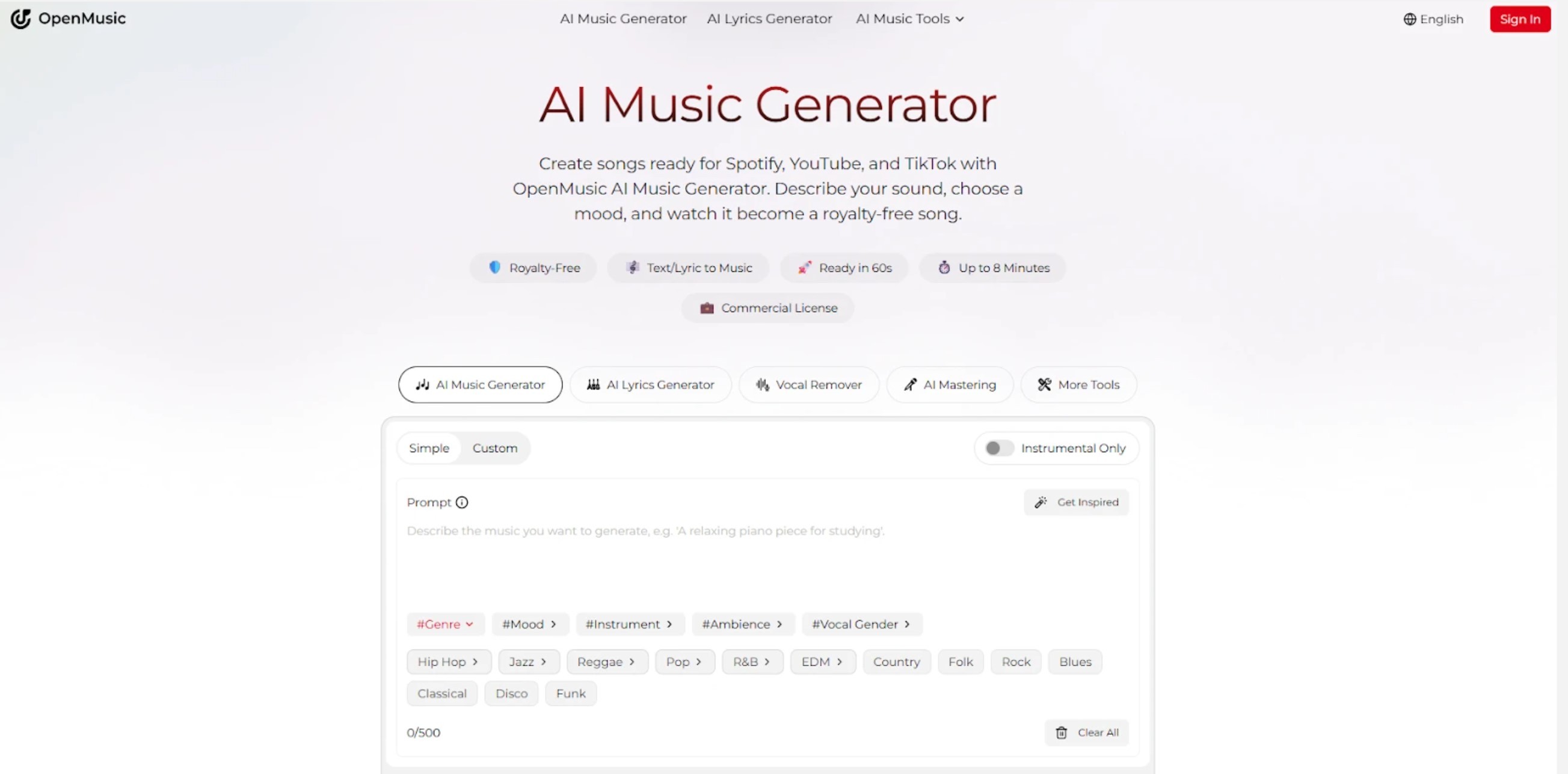
What OpenMusic AI Offers: A Practical Overview
OpenMusic AI exemplifies how modern AI music tools bring data-driven music creation to end users. Its capabilities include:
Text-to-music generation: Provide a text description, mood, or lyrics — and the system can generate a full song. This covers genres from electronic dance music (EDM), hip-hop, lo-fi, jazz, ambient, to cinematic orchestral pieces.
Instrumental and multi-genre flexibility: Whether you need a lo-fi beat for a YouTube video or a cinematic soundtrack, OpenMusic AI supports varied styles.
Post-production tools: After generating base tracks, users can apply AI-powered mixing, mastering, and track separation (e.g. vocal removal, instrument isolation).
Export and licensing ready: Tracks generated are provided royalty-free and come with licensing terms compatible with commercial release on platforms like streaming services — eliminating legal/licensing burdens.
Accessibility and ease of use: The process doesn’t require deep musical knowledge or expensive equipment. Users can create songs with simple prompts or lyric input.
Thus, OpenMusic AI acts as a full-stack AI Music Generator: from conception (ideas, text) to final master and ready-to-publish output.
How One Uses an AI-Powered Music Tool: Typical Workflow
Define concept or mood — maybe “chill lo-fi track for streaming video,” or “cinematic trance with piano and strings.”
Enter prompt or lyrics — as text or mood tags.
Choose genre or instrumentation — select style: hip-hop, ambient, EDM, jazz, etc.
Let the AI generate base tracks — the AI creates melody, harmony, rhythm, and arrangement.
Use built-in editing tools — optionally separate stems, refine structure, apply mixing and mastering.
Export final audio — download royalty-free track with licensing for commercial use.
Publish or integrate — upload to streaming platforms, use in video, games, or other media.
This workflow drastically simplifies music creation compared to traditional studio-based production.
Benefits and Limitations: A Balanced View
Advantages
Cost efficiency: No need for expensive studio time or live musicians. Ideal for solo creators, indie artists, or content creators on tight budgets.
Speed and agility: A track can be produced in minutes. Great for social media, quick content cycles, or dynamic media.
Lower barrier to entry: Anyone — even without music training — can create original music. This democratizes music production.
Variety and experimentation: Users can try different genres or combinations easily. This can lead to creative exploration otherwise hard to realize.
Royalty-free and licensing clarity: AI-generated tracks often come with straightforward licensing, simplifying monetization.
Constraints
Artistic depth may be lower: While AI can approximate genre conventions, it may struggle with highly emotional or deeply human musical expression. AI-generated music sometimes lacks the nuance of human-composed pieces.
Originality vs. similarity: Because AI is trained on existing music data, outputs may unintentionally echo patterns seen before. Novelty can be limited.
Limited control over nuance: Fine-grained creative control (e.g. expressive timing, subtle dynamic variation) may remain challenging.
Licensing and copyright ambiguity (in some tools): Not all AI-generated tracks are guaranteed safe for all commercial uses — careful review is needed. (In the case of OpenMusic AI, licensing is explicit.)
Dependence on dataset biases: If training data skews toward certain genres or cultures, AI output may reflect those biases — limiting diversity.
Who Gains Most: Target User Profiles
Independent musicians and producers — those lacking access to studios or collaborators can now create full tracks solo.
Content creators (video, social media, games) — need background music, soundtracks, or jingles quickly and affordably.
Game developers and multimedia producers — want royalty-free music assets without hiring composers.
Hobbyists and experimental artists — curious minds wanting to explore music creation without steep learning curves.
Small businesses and marketers — needing custom audio for ads, promos, or brand content without licensing overhead.
In short: anyone who needs music — but lacks resources or wants efficiency — can benefit.
Why This Matters for the Music Industry and Digital Market
AI music generation tools mark a shift in the music industry’s economics and structure. As AI-powered tools proliferate:
More music will flood digital platforms. The volume of releases may rise significantly.
Costs of production drop. This fosters democratization: artists without traditional support can participate.
Licensing becomes simpler. Royalty-free AI-generated tracks reduce legal friction for content-driven creators.
Diversity may increase. With low barriers, niche genres, hybrid styles, and experimental music may flourish.
New business models emerge. For example: custom music-as-a-service, dynamic soundtracks for games or content, AI-aided collaboration platforms, automated soundtrack generation, etc.
Industry reports (e.g. an “AI Music Application Industry Report (2024)” ) suggest AI-based music generation is becoming a real driver of growth for digital music markets. AI tools simplify production workflows and enable scalable monetization.
Also, research like PopMAG: Pop Music Accompaniment Generation demonstrates that multi-track harmony modeling via AI can achieve results that approximate human composition in subjective tests.
Together, these developments hint that data-powered AI music generation will play an increasingly central role in the future of music creation and distribution.
Realistic Aspirations and Best-Use Cases
AI music generators are not yet a full replacement for human artistry — at least not for deeply expressive, emotionally rich compositions. But they excel in contexts where speed, convenience, and versatility matter. Ideal scenarios include:
Background music for videos, podcasts, or short films.
Game and multimedia asset production needing lots of loops, ambience, or mood tracks.
Demo creation or conceptual sketches. Artists can prototype quickly before engaging deeper production.
Independent release of instrumental tracks, lo-fi beats, ambient music, electronic music — where nuance matters less.
Content marketing, advertising, social media, where high volume and quick turnaround outweigh artistic depth.
Final Thoughts: Data-Fueled Creativity in a New Era
We are witnessing a fundamental shift in how music can be made. Data and AI together lower barriers. Tools like OpenMusic AI exemplify what is possible: from idea to final track in minutes; from concept to commercial-ready music without studios or musicians. This does not make human composers obsolete — but it democratizes music creation.
In this evolving landscape, AI music generators serve as powerful enablers. They give creators choice, agility, and access. For many, these tools will open doors previously closed. As datasets grow, algorithms improve, and models evolve, the quality and variety of AI-generated music will likely increase.
The future likely belongs to hybrid workflows: human creativity plus AI acceleration. Data-driven tools will augment, not replace, human artistry. For independent artists, content creators, and anyone seeking to create music, this is an exciting moment.
Whether you’re a hobbyist, a small team, or a solo creative — now you can dream music into existence, using data and AI as your collaborators.
The Rise of Data-Driven Music Creation
In the past decade, music production started a transformation. Traditional methods relied on human composers, musicians, and physical instruments. Now, data-driven tools and artificial intelligence (AI) are reshaping the process. AI music creators are growing more powerful and accessible. These systems rely heavily on large datasets and smart algorithms. The result: anyone can generate music with a few clicks. This trend is changing how music is made, distributed, and consumed.
The Challenge in Conventional Music Production
Producing professional music is costly and slow. It needs skilled musicians, studios, equipment, and time. Independent artists or small teams often lack these resources. Also, coordinating multiple tracks, mixing, mastering, and licensing makes things complex. For many creators, producing original music remains out of reach. This limits diversity, slows release frequency, and raises entry barriers.
Moreover, as streaming platforms and social media drive demand for new songs constantly, traditional workflows struggle to keep up. Artists may feel pressured to churn out content quickly. In such a fast-paced context, old methods are inefficient. There is a clear need for tools that can speed up music creation, reduce cost, and simplify licensing.
How Smart Data Powers AI Music Tools
At the core of modern AI music generators lies data — lots of it. High-fidelity music recordings, MIDI data, metadata, genre tags, and structural annotations feed machine-learning models. Models learn patterns: chord progressions, rhythms, instrumentation, genre characteristics. With enough training data, AI can generalize: it can create original compositions that follow genre conventions. This helps the AI produce music that feels coherent and professional.
For example, open-source research frameworks like Music Representing Corpus Virtual (MRCV) enable experiments in generative music, sound design, and virtual instrument creation. They show how leveraging curated datasets helps generate diverse music and sound assets.
Similarly, advanced models such as those behind OpenMusic AI use diffusion-based or deep learning approaches, trained on large, high-quality audio datasets. These systems can handle multi-track harmony, realistic instrumentation, and varied genres — not just simple looped beats. This data grounding allows AI to “understand” the building blocks of music before recombining them creatively.
What OpenMusic AI Offers: A Practical Overview
OpenMusic AI exemplifies how modern AI music tools bring data-driven music creation to end users. Its capabilities include:
Text-to-music generation: Provide a text description, mood, or lyrics — and the system can generate a full song. This covers genres from electronic dance music (EDM), hip-hop, lo-fi, jazz, ambient, to cinematic orchestral pieces.
Instrumental and multi-genre flexibility: Whether you need a lo-fi beat for a YouTube video or a cinematic soundtrack, OpenMusic AI supports varied styles.
Post-production tools: After generating base tracks, users can apply AI-powered mixing, mastering, and track separation (e.g. vocal removal, instrument isolation).
Export and licensing ready: Tracks generated are provided royalty-free and come with licensing terms compatible with commercial release on platforms like streaming services — eliminating legal/licensing burdens.
Accessibility and ease of use: The process doesn’t require deep musical knowledge or expensive equipment. Users can create songs with simple prompts or lyric input.
Thus, OpenMusic AI acts as a full-stack AI Music Generator: from conception (ideas, text) to final master and ready-to-publish output.
How One Uses an AI-Powered Music Tool: Typical Workflow
Define concept or mood — maybe “chill lo-fi track for streaming video,” or “cinematic trance with piano and strings.”
Enter prompt or lyrics — as text or mood tags.
Choose genre or instrumentation — select style: hip-hop, ambient, EDM, jazz, etc.
Let the AI generate base tracks — the AI creates melody, harmony, rhythm, and arrangement.
Use built-in editing tools — optionally separate stems, refine structure, apply mixing and mastering.
Export final audio — download royalty-free track with licensing for commercial use.
Publish or integrate — upload to streaming platforms, use in video, games, or other media.
This workflow drastically simplifies music creation compared to traditional studio-based production.
Benefits and Limitations: A Balanced View
Advantages
Cost efficiency: No need for expensive studio time or live musicians. Ideal for solo creators, indie artists, or content creators on tight budgets.
Speed and agility: A track can be produced in minutes. Great for social media, quick content cycles, or dynamic media.
Lower barrier to entry: Anyone — even without music training — can create original music. This democratizes music production.
Variety and experimentation: Users can try different genres or combinations easily. This can lead to creative exploration otherwise hard to realize.
Royalty-free and licensing clarity: AI-generated tracks often come with straightforward licensing, simplifying monetization.
Constraints
Artistic depth may be lower: While AI can approximate genre conventions, it may struggle with highly emotional or deeply human musical expression. AI-generated music sometimes lacks the nuance of human-composed pieces.
Originality vs. similarity: Because AI is trained on existing music data, outputs may unintentionally echo patterns seen before. Novelty can be limited.
Limited control over nuance: Fine-grained creative control (e.g. expressive timing, subtle dynamic variation) may remain challenging.
Licensing and copyright ambiguity (in some tools): Not all AI-generated tracks are guaranteed safe for all commercial uses — careful review is needed. (In the case of OpenMusic AI, licensing is explicit.)
Dependence on dataset biases: If training data skews toward certain genres or cultures, AI output may reflect those biases — limiting diversity.
Who Gains Most: Target User Profiles
Independent musicians and producers — those lacking access to studios or collaborators can now create full tracks solo.
Content creators (video, social media, games) — need background music, soundtracks, or jingles quickly and affordably.
Game developers and multimedia producers — want royalty-free music assets without hiring composers.
Hobbyists and experimental artists — curious minds wanting to explore music creation without steep learning curves.
Small businesses and marketers — needing custom audio for ads, promos, or brand content without licensing overhead.
In short: anyone who needs music — but lacks resources or wants efficiency — can benefit.
Why This Matters for the Music Industry and Digital Market
AI music generation tools mark a shift in the music industry’s economics and structure. As AI-powered tools proliferate:
More music will flood digital platforms. The volume of releases may rise significantly.
Costs of production drop. This fosters democratization: artists without traditional support can participate.
Licensing becomes simpler. Royalty-free AI-generated tracks reduce legal friction for content-driven creators.
Diversity may increase. With low barriers, niche genres, hybrid styles, and experimental music may flourish.
New business models emerge. For example: custom music-as-a-service, dynamic soundtracks for games or content, AI-aided collaboration platforms, automated soundtrack generation, etc.
Industry reports (e.g. an “AI Music Application Industry Report (2024)” ) suggest AI-based music generation is becoming a real driver of growth for digital music markets. AI tools simplify production workflows and enable scalable monetization.
Also, research like PopMAG: Pop Music Accompaniment Generation demonstrates that multi-track harmony modeling via AI can achieve results that approximate human composition in subjective tests.
Together, these developments hint that data-powered AI music generation will play an increasingly central role in the future of music creation and distribution.
Realistic Aspirations and Best-Use Cases
AI music generators are not yet a full replacement for human artistry — at least not for deeply expressive, emotionally rich compositions. But they excel in contexts where speed, convenience, and versatility matter. Ideal scenarios include:
Background music for videos, podcasts, or short films.
Game and multimedia asset production needing lots of loops, ambience, or mood tracks.
Demo creation or conceptual sketches. Artists can prototype quickly before engaging deeper production.
Independent release of instrumental tracks, lo-fi beats, ambient music, electronic music — where nuance matters less.
Content marketing, advertising, social media, where high volume and quick turnaround outweigh artistic depth.
Final Thoughts: Data-Fueled Creativity in a New Era
We are witnessing a fundamental shift in how music can be made. Data and AI together lower barriers. Tools like OpenMusic AI exemplify what is possible: from idea to final track in minutes; from concept to commercial-ready music without studios or musicians. This does not make human composers obsolete — but it democratizes music creation.
In this evolving landscape, AI music generators serve as powerful enablers. They give creators choice, agility, and access. For many, these tools will open doors previously closed. As datasets grow, algorithms improve, and models evolve, the quality and variety of AI-generated music will likely increase.
The future likely belongs to hybrid workflows: human creativity plus AI acceleration. Data-driven tools will augment, not replace, human artistry. For independent artists, content creators, and anyone seeking to create music, this is an exciting moment.
Whether you’re a hobbyist, a small team, or a solo creative — now you can dream music into existence, using data and AI as your collaborators.
More Update
import StickyCTA from "https://framer.com/m/StickyCTA-oTce.js@Ywd2H0KGFiYPQhkS5HUJ"



